There was a time when LEDs were manufactured, packed in a little plastic casing, and then installed on the board. The process was secure, but it heavily limited the number of LEDs you could put on a single board.
Times have changed since then, and so has the technology. Technology is focussing on the small size of chip, so small components are required that fit onto it.
This drive has led to the birth of Chip on-board LEDs. These are the most common form of LED applications today. However, not many people are aware of the technology behind it and how it functions.
In this article, we will discuss what is Chip onboard LED and how it is used in today’s technology.
What are Chip on Board (COB) LEDs?
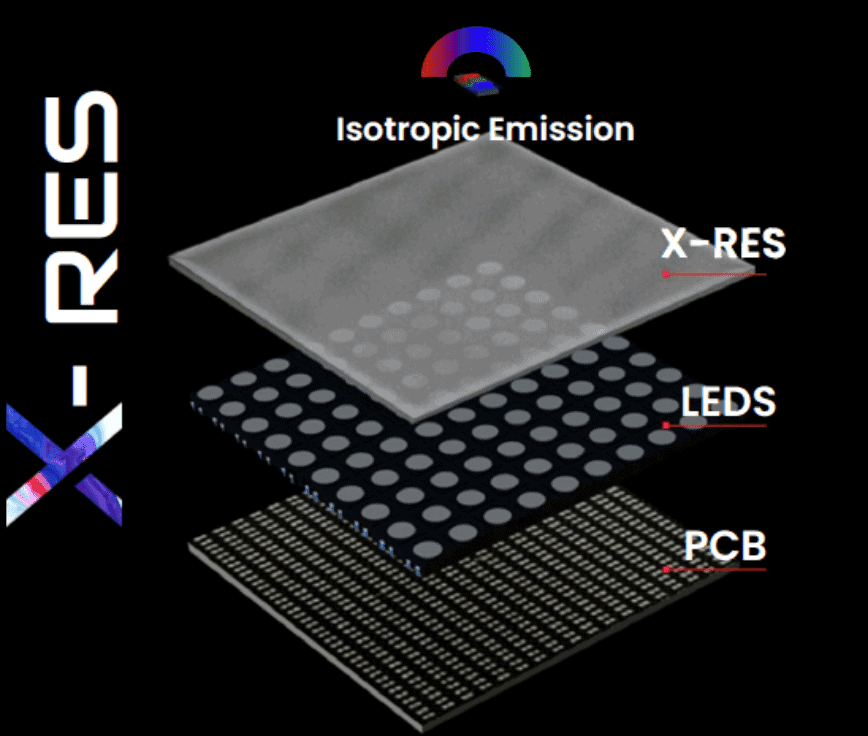
 COB LED refers to Chip on Board LED, also known as Glue on Board LED or Resin on Board LED. In this LED technology a bare LED chip (light emitting diode) is directly mounted on the board and then sealed with epoxy glue or resin.
COB LED refers to Chip on Board LED, also known as Glue on Board LED or Resin on Board LED. In this LED technology a bare LED chip (light emitting diode) is directly mounted on the board and then sealed with epoxy glue or resin.
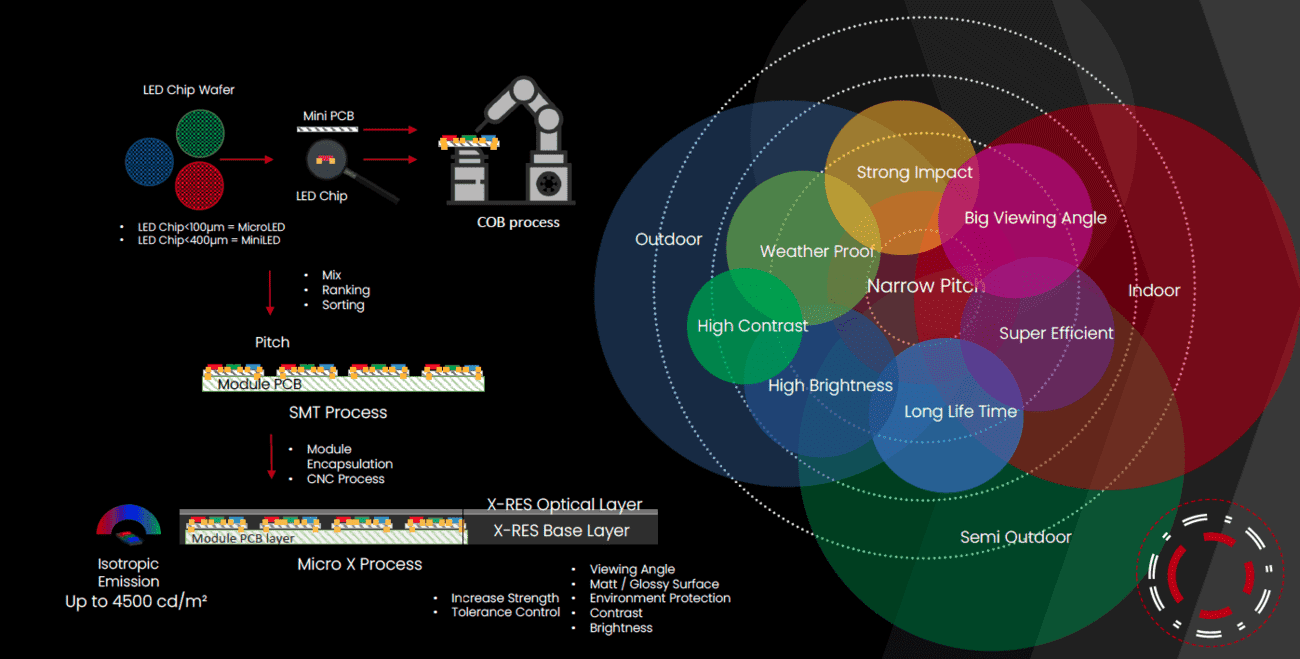
The mounting takes place by keeping LED chip in direct contact on a substrate such as Silicon Carbide or Sapphire. Since no individual protection is required, multiple diodes are packed and mounted together, then sealed with a resin.
This results in a very dense LED system where the board has a higher number of LEDs in a smaller area. Usually, nine or more LED chips are mounted together on the board as a single module.
With COB LED, you see the LED module as a single panel rather than an assortment of different identifiable LEDs.
While the LED chips mounted on board are not given individual protection, the resin used is so strong that the LED module is protected against impacts, water, and any environmental elements.
What is the Difference Between LED and COB LED?
In these earlier LED technologies, each individual LED chip was soldered on the printed circuit board (PCB) individually. This lead to a lot of contact points of the resulting module.
Additionally, older LED technologies highly limited the number of diodes you could have in a single module. Since each diode required an exclusive circuit and protection, you could have only one to three diodes at the most.
Is COB LED better than conventional LED?
Chip on Board LED can produce LED arrays with significant improvement on the conventional LED technology such as Surface Mounted Device LEDs (SMD LEDs) and Dual In-Line Package LEDs (DIP LEDs).
In COB LED, there are a number of LED chip in direct contact with the board. Since a bare LED chip is used (which are very small size components), you can stack a lot of diodes together in a single module.
Therefore, this results in higher intensity of the lights and a higher packing density as well. When you look at a COB LED, you cannot identify individual diodes on the surface.
What are COB LEDs?
There are many benefits that Chip on Board LED offers over older LEDs. These include:
High Brightness:
In chip on board LEDs, multiple led chips are stacked together in a tight space. The much higher packing density results in a very high brightness output of the module.
Resolution:
Due to close distances high uniformity and a much higher packing density, it is hard to distinguish individual diodes on the panel. Therefore, Chip on board LED makes it possible to produce LED arrays with a very high resolution.
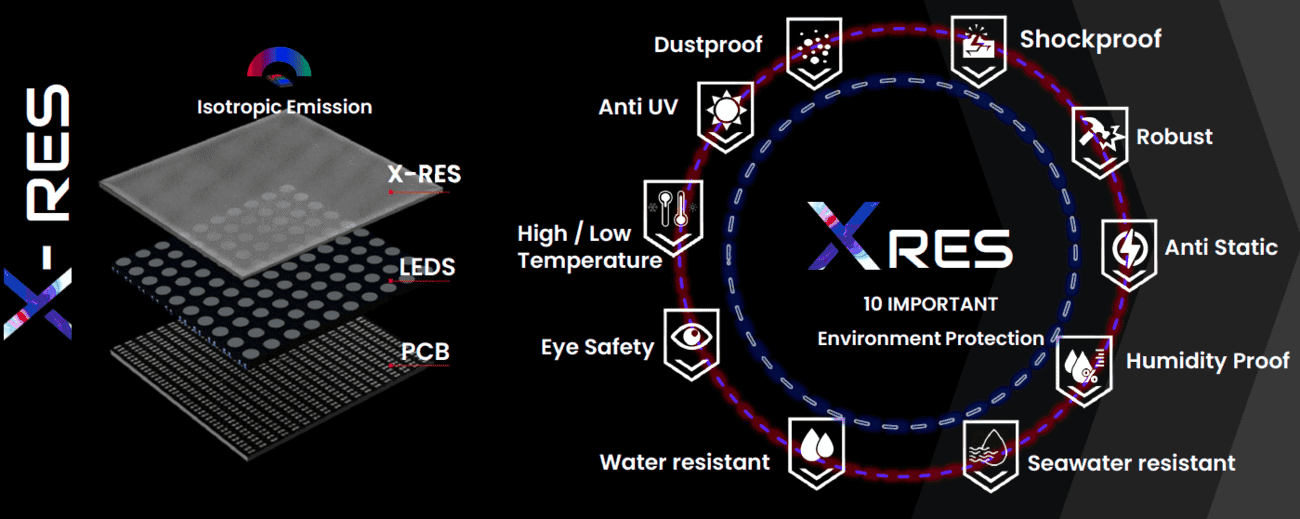
Protection:
The resin used in the COB LED technology provides very high protection to the panels. The plastic packing in the conventional LED chips can break but the resin in COB LEDs is resistant to impacts.
Resins in COB have superior thermal performance, meaning that your LED chip will not burn out. As a matter of fact, X Res LEDs are even resistant to water and humidity. You could immerse the LED module in water, and anything protected by the resin will not get wet.
Contrast:
Since a given area contains a large number of controllable LED chips with high uniformity, the resulting display panel has a very high contrast than conventional SMD LEDs.
Wide Angle Beam:
COB LEDs can create a wide-angle higher quality beam due to their adjustable directional nature and higher brightness. This makes them useful in street lighting solutions and wide viewing angle displays.
What are the Uses of COB LEDs?
There are many applications of COB LED technology in the LED market, such as:
- Displays
- LED lights for home
- Streetlights
- Downlights
- Fog lights for stadiums
- High output track lights
- Camera Flash
- Light strip
- Decorative lights
Does COB LED Technology Have Any Disadvantages?
While COB LED technology is the best available one right now, it has some concerns that experts have noticed.
For one thing, Chip on Board LED uses glue on top of the diodes for protection. This creates a thick layer for the light to pass, which can cause shifts in wavelength. It may lead to decreased color uniformity and shifts in color from their intended value.
Additionally, COB LEDs require a good heat sink for their proper functioning. Otherwise, the heat buildup under the glue can affect the diodes that are in direct contact with the board.
Fortunately, improved technologies like the X-Res have eliminated these disadvantages from the COB LEDs by improved properties and superior thermal performance.
How Long Does a COB LED Last?
Generally, COB LEDs can easily last about 50,000 hours. This means that if you are using the LED for 12 hours a day, you can expect it to last for 4167 days, which is roughly eleven and a half years.
This is a significantly longer lifespan than other LED technology and lighting solutions that are available right now.
Are COB LEDs Dimmable?
Yes, it is possible to dim a COB LED. However, you require a dimming driver and a COB LED circuit that is compatible with dimming functioning. Nowadays, even dim-to-warm COB LEDs are available for aesthetic applications.
Endnotes
Chip on board COB technology is one of the most evolved forms of LED right now. It has so much to offer, with very few disadvantages.
Even the factors that might seem like a disadvantage can be avoided by combining the COB technology LED arrays with a direct contact resin such as X-RES.